Author: H.-W. Schiffer
In a guest article, Dr. Hans-Wilhelm Schiffer discusses the characteristics of forecasts and scenarios for the energy transition in various studies. In doing so, he critically classifies the approaches pursued by the institutions mentioned. Originally, the article appeared in 2021 under the title “Forecasts and scenarios for global energy supply as the basis for climate policy implications” in the magazine VGB PowerTech. This is the second part of the series of articles.
In October 2021, the International Energy Agency (IEA) presented the World Energy Outlook 2021 (WEO-2021). The publication was to be understood as a clear signal to the UNFCCC Conference of the Parties (COP26), which was held in Glasgow in November 2021. In presenting this comprehensive study, the following points were highlighted by the IEA:
- The commitments made by states to limit greenhouse gas emissions must be tightened.
- The developing and emerging countries are crucial for the future development of the energy system. Their investments in clean energies must be increased – with the support of the industrialized countries.
- Addressed to investors: Future investments in fossil fuels harbor potential losses, while investments in clean energies promise profits.
Professor Dr. Hans-Wilhelm Schiffer
Lecturer at RWTH Aachen University, Member of the Studies Committee, World Energy Council, London and Chairman of the Energy for Germany editorial group at the Weltenergierat – Deutschland, Berlin
Four normative and exploratory scenarios
When these points are addressed in policies, the transformation to a globally sustainable energy supply should be accelerated. The existing challenge of achieving the Paris climate goals is illustrated using two exploratory and two normative scenarios.
These four scenarios can be characterized as follows:
The Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) takes into account the measures that have actually been put into effect or are at least being implemented in order to achieve announced energy and climate policy goals. One example is the Fit-for-55 Package, which was proposed by the European Commission in July 2021. It represents an exploratory approach to the future development of the energy supply, which will lead to a global temperature increase of 2.6 degrees Celsius by the year 2100 compared to the pre-industrial level.
The Announced Pledges Scenario (APS) takes into account all climate commitments made by governments worldwide, including the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and the longer-term Net Zero targets, and assumes that these will be met in full and on time. According to this scenario, the global temperature increase remains limited to 2.1 degrees Celsius until 2100.
The Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS) follows an approach that puts the energy system on the right path to meet the most important sustainability goals. This includes everyone’s access to affordable energy by 2030 and a drastic reduction in pollution in the soil, water and air. With regards to climate-relevant gases, advanced economies will achieve net zero emissions by 2050, China by 2060 and all other countries by 2070 at the latest. For this normative scenario, a maximum global temperature increase of 1.7 degrees Celsius is determined in 2050.
The Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) is a normative scenario that shows a narrow but viable path for the global energy system to achieve net zero emissions by 2050, with advanced economies implementing this before others. This scenario also meets the requirements of the other energy-related UN goals mentioned. In the NZE, the peak in the global temperature rise in 2050 will be 1.5 degrees Celsius.
The results obtained for the various scenarios differ greatly. The developments up to the year 2050 are outlined below.
STEPS scenario: CO2 emissions fall insufficiently
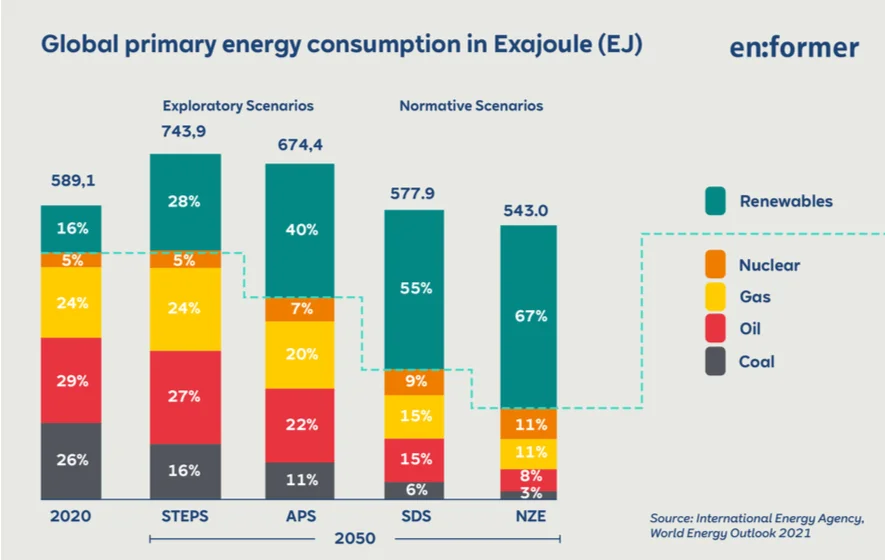
In the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) there is a change in the energy supply system. Due to global population growth from 7.75 billion today to 9.7 billion in 2050 and an expected increase in economic output, especially in developing and emerging countries, global energy consumption may increase by 26 percent by 2050 compared to levels in 2020. The share of renewable energies in global primary energy consumption will increase from 16 percent in 2020 to 28 percent in 2050. Nevertheless, fossil energies, i.e. coal, oil and natural gas, will still cover two thirds of global primary energy consumption in 2050 – compared to 79 percent in 2020. As in 2020, nuclear energy will then account for 5 percent.
The capture and use or storage of CO2 (Carbon Capture and Usage / Storage – CCUS) makes only a very limited contribution to reducing CO2 emissions in this scenario. According to this scenario, the total CO2 emissions of 33.9 billion tonnes (billion t) in 2050 are just below 2020 with 34.2 billion t. As a consequence, global temperatures will rise by 2.6 degrees Celsius by 2100 compared to pre-industrial levels.
APS Szenario: Limited increase in primary energy consumption
According to the Announced Pledges Scenario (APS), global CO2 emissions will drop by around 40 percent to 20.8 billion t in 2050. But this path is still associated with a temperature increase of 2.1 degrees Celsius by 2100. In contrast to STEPS, the global increase in primary energy consumption will remain limited to 14 percent by 2050. Renewable energies have a share of almost 40 percent . The contribution of nuclear energy increases to 7 percent .
Fossil energies account for 53 percent , with significantly greater role being assumed for CCUS compared to the STEPS. The currently announced commitments, however, only cover less than 20 percent of the gap in emissions reduction that must be closed by 2030 in order to keep the 1.5 degree target within reach. Even if the commitments announced by mid-2021 are met, there remains a clear ambition gap to the Paris climate targets.
The normative scenarios: SDS and NZE
In the two normative scenarios – these are the Sustainable Development Scenario (SDS) and the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario (NZE) – the IEA shows how this gap could be closed according to the model calculations carried out. In the report, the IEA identifies four crucial measures:
- The wind and solar expansion is to be doubled compared to the APS.
- Expansion of other CO2-free generation, including nuclear energy, where accepted.
- Expansion of the electricity infrastructure and all forms of improving system flexibility, including hydropower.
- Rapid end to the use of coal in plants without CCUS.
- Expansion of the use of electricity in the transport sector and in the heating of buildings.
Accelerating the decarbonization of the electricity mix is seen as the single greatest lever politicians have at their disposal. Half of the additional emissions reduction could be achieved at no cost to consumers.
This is to be achieved by improving material efficiency and changing consumer behavior. According to the IEA, 80 percent of the energy efficiency increase in the NZE over the next decade will lead to cost reductions for consumers.
This is seen as a very cost-efficient measure, especially in the value chain of the oil and natural gas industry.
All technologies required to reduce emissions by 2030 in accordance with the NZE are available. However, half of the emissions reduction that the NZE claims to be achieved by 2050 will have to be achieved by technologies that are still in the demonstration or prototype phase. This applies in particular to technologies in the iron and steel industry, cement and other energy-intensive sectors, as well as long-distance transport. The development of hydrogen based technologies and the implementation of CCUS are seen as critical.
In order to get the world on the path to the 1.5 °C target, investments in clean energy projects and the necessary infrastructure amounting to nearly 4 trillion US $ per year are required. Most of the capital for the investment needs to be financed by the private sector – based on market signals and the framework set by politics.
In addition, public financial institutions are also seen as necessary, such as international development banks, to trigger investments where private players do not see a sufficient balance between risk and chance.
Development of fossil energy sources
The development of the individual energy sources is very different. The global consumption of coal decreases in all scenarios. But the difference between a 10 percent decrease in ASP by 2030 and a 55 percent decrease in NZE is determined by the speed at which coal is displaced in the electricity sector. The options are shutting down existing capacities, retrofitting with CCUS and adding CO2- free or fuels with low-CO2 emissions such as biomass or ammonia.
The oil consumption will decrease in the future – and this for the first time in current model calculations of the IEA, even if there are strong deviations between the scenarios with regard to the characteristics of the course. In STEPS, peak oil demand is expected in the mid-2030s, in APS shortly after 2025. In order to achieve NZE, oil consumption must drop to 25 mb/d by the middle of the century. This corresponds to a decrease of around 75 percent.
Demand for natural gas will increase in all scenarios over the next five years. After that, however, the paths shown in the various scenarios differ greatly. In NZE, the development of new oil and gas fields is no longer considered necessary – beyond the projects that are already under development. In this scenario, global natural gas consumption will decrease by more than half by 2050 compared to the 2020 level.
Development of Renewable Energies
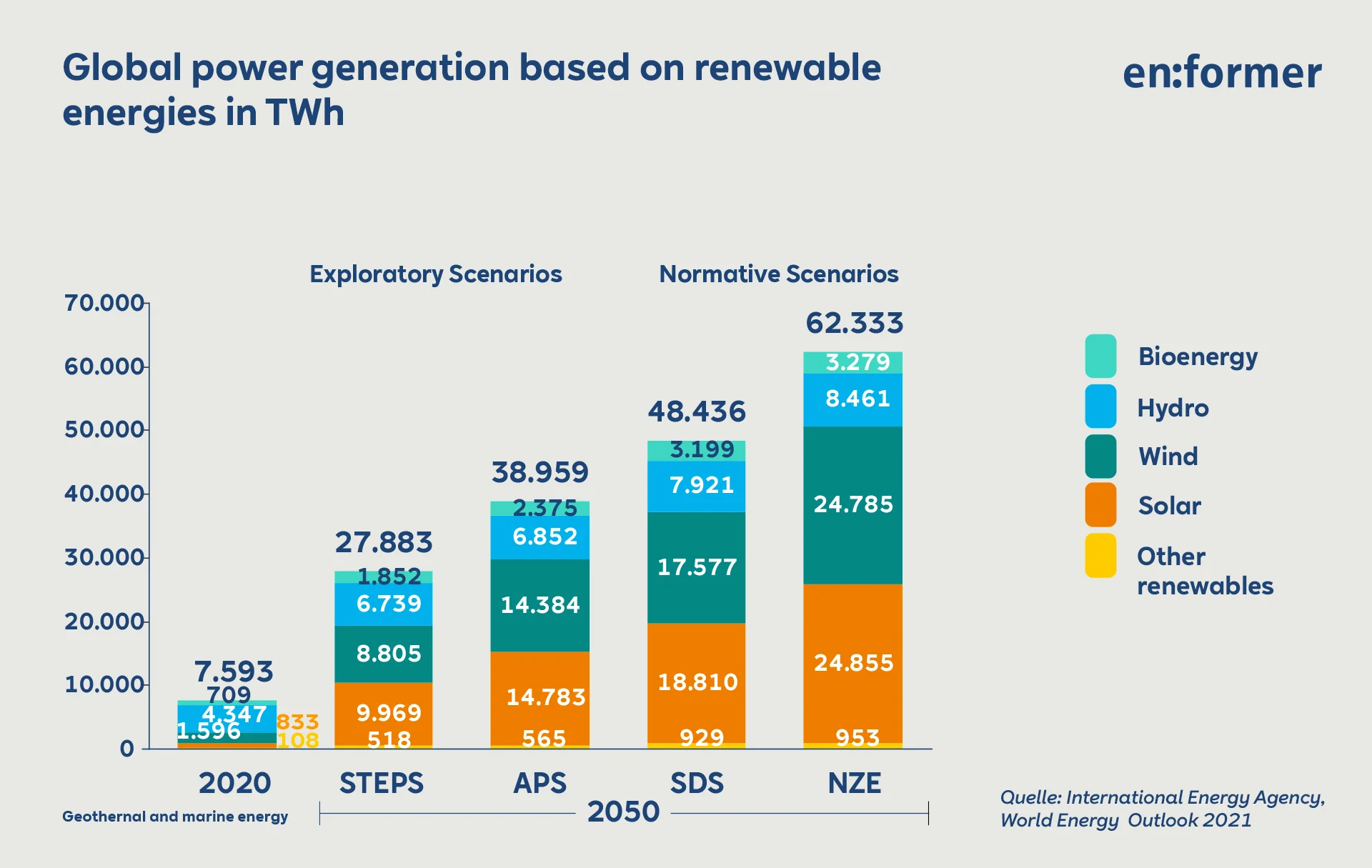
Renewable energies increase significantly in all scenarios – most strongly in the NZE. In this scenario, renewable energies account for 67 percent of the primary energy consumption in 2050. Solar energy has increased twenty-three times compared to the level of 2020, and wind power has increased fifteen times. For hydropower and biomass – as well as for nuclear energy – a doubling of the absolute contribution is expected. Nuclear energy then has a share of 11 percent in covering primary energy consumption. Fossil energies only retain a share of 22 percent.
In global power generation, the share of renewable energies in the NZE will even increase to 88 percent in 2050. 35 percentage points of this will be attributable to solar and wind, 12 percentage points to hydropower, 5 percentage points to bio-energy and 1 percentage point to geothermal energy. A share of 8 percent is reported for nuclear energy. Hydrogen and ammonia come to 2 percent. This also applies to coal and natural gas with CCUS.
Expansion of renewables in the NZE scenario
According to NZE, there will be 240 million PV roof top systems and 1.6 billion electric vehicles worldwide in 2050. This requires battery storage, the expansion of power grids and controllable systems based on sources with low CO2 emissions, such as hydropower, geothermal energy, bio-energy, hydrogen and ammonia as well as small modular nuclear energy reactors. Increasing digitization can support demand management and the flow of data in general.
Rare earths and hydrogen-based fuels will in future become essential elements in international energy trading. Their combined share in energy trading will increase from 13 percent today by 2050 to 25 percent in the APS and more than 80 percent in the NZE.
The NZE sees great market opportunities for manufacturers of wind turbines, solar panels, lithium-ion batteries, electrolysers and fuel cells. With a volume of over US $ 1 trillion by 2050, an order of magnitude comparable to the current global oil market is expected.
IEA: Governments must react
The IEA sees governments in the driver’s seat in steering future developments, but municipalities, companies, investors and consumers also have an important role to play. What is decisive for the very different results in the four scenarios is the assumed pricing of CO2. In STEPS, an increase in CO2 prices by 2050 to up to US $ 90 (2020) per ton in industrialized countries (including for the EU) is set as a model input. In the ASP it is US $ 200 (2020) per ton in industrialized countries with net zero emission obligations, in China it is US $ 160 (2020) per ton and in developing and emerging countries with net zero pledges it is US $ 160 (2020) per ton.
In the SDS, the same CO2 price is set as the model input for all countries with net zero emission obligations as in the APS, in other industrialized countries it is 160 US $ (2020) per ton and in emerging and developing countries 95 US $ (2020 ) per ton. The highest CO2 prices are set for the year 2050 in the NZE, namely 250 US $ (2020) per ton in the industrialized countries, 200 US $ (2020) per ton in the larger emerging countries and 55 US $ (2020) per ton in other emerging and developing countries. This shows that carbon pricing has a key role to play in meeting the Paris climate targets.
Photo credit: © shutterstock.com, Bjoern Wylezich